Roller Conveyor Manufacturer
Home > Roller Conveyor
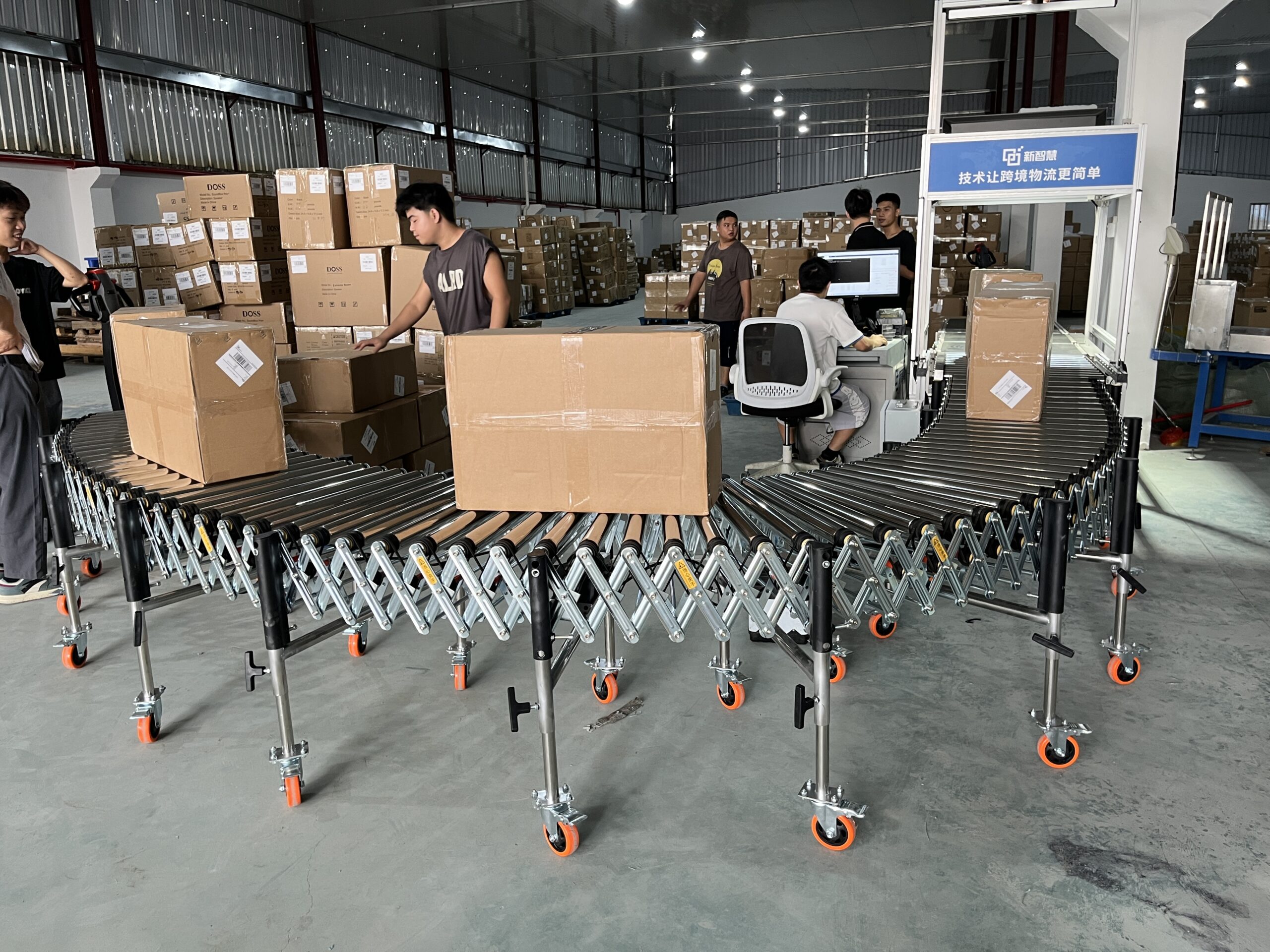
Professional roller conveyor manufacturer and supplier offering high-quality gravity and powered roller conveyor solutions for efficient material handling in warehouses and production lines.
Our Roller Conveyor Products
560 mm
1100 mm
120 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
Bagged Goods
525 mm
1500 mm
80 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
700 mm
2000 mm
100 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
1050 mm
3000 mm
80 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
525 mm
1500 mm
50 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
Bagged Goods
485 mm
1700 mm
50 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
Bagged Goods
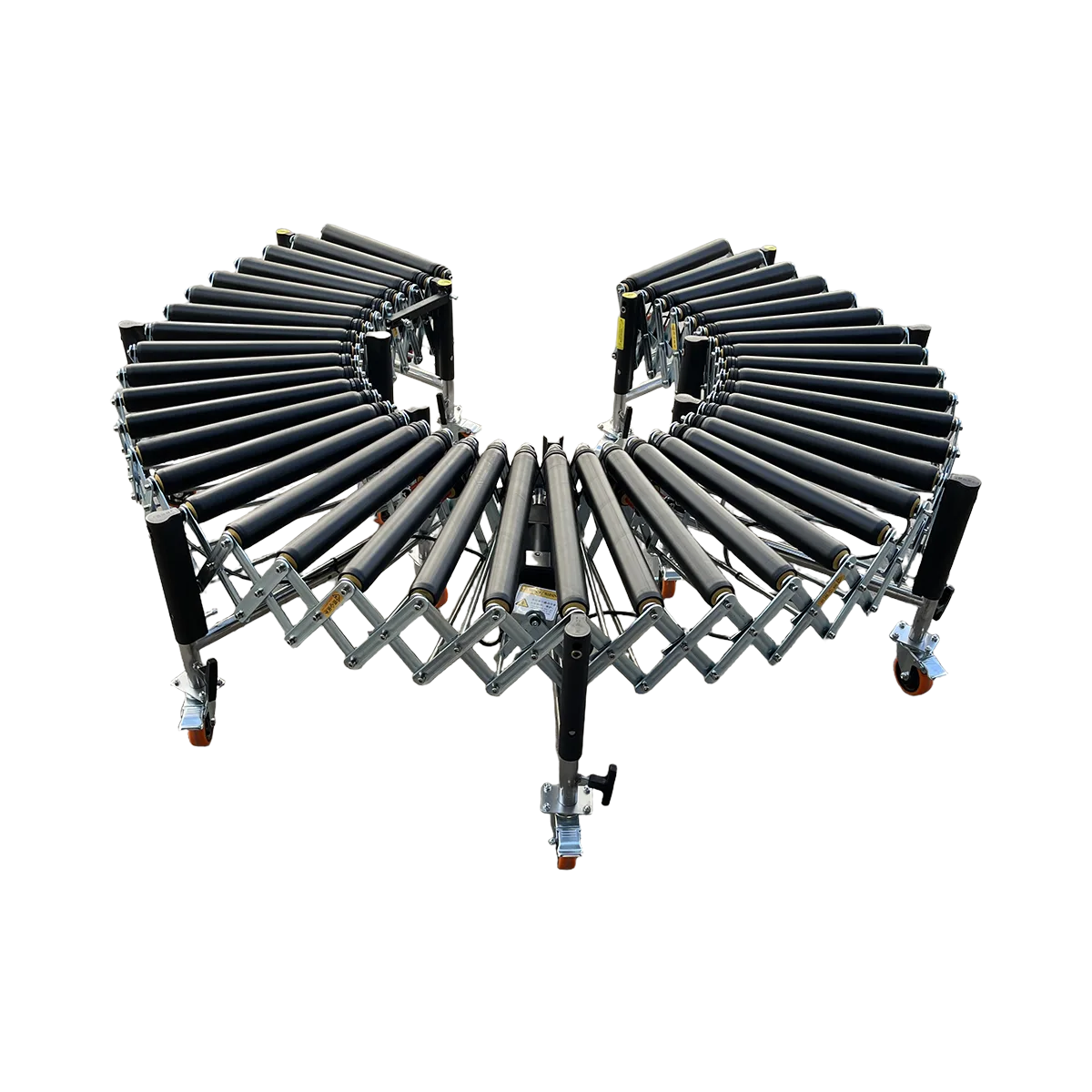
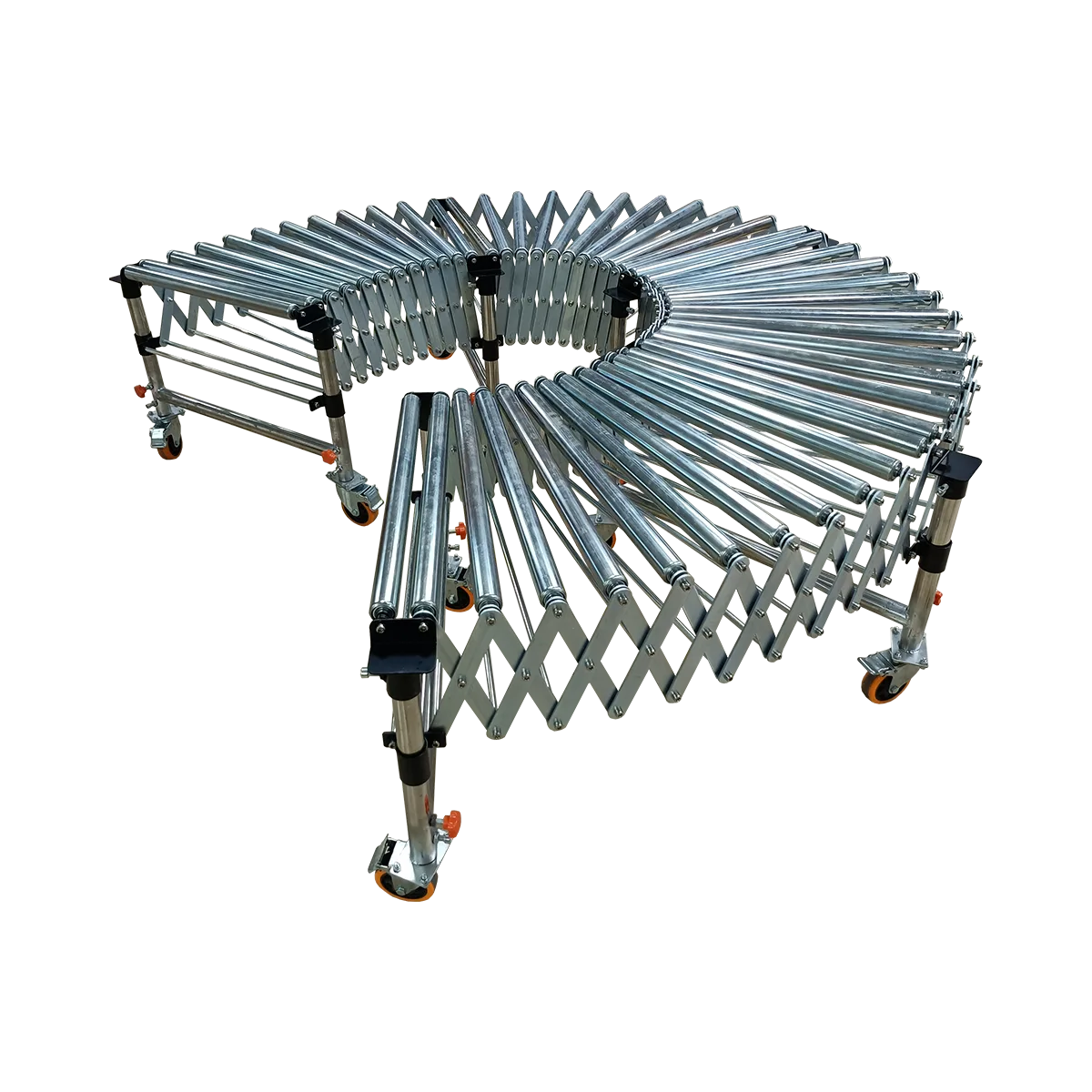
Roller conveyors represent one of the most versatile and widely-used material handling systems in modern logistics and manufacturing. As a professional roller conveyor manufacturer, we offer comprehensive conveying solutions designed to streamline operations, reduce manual handling, and increase throughput efficiency. Our range includes both powered and gravity systems, engineered for various industrial applications and environments.
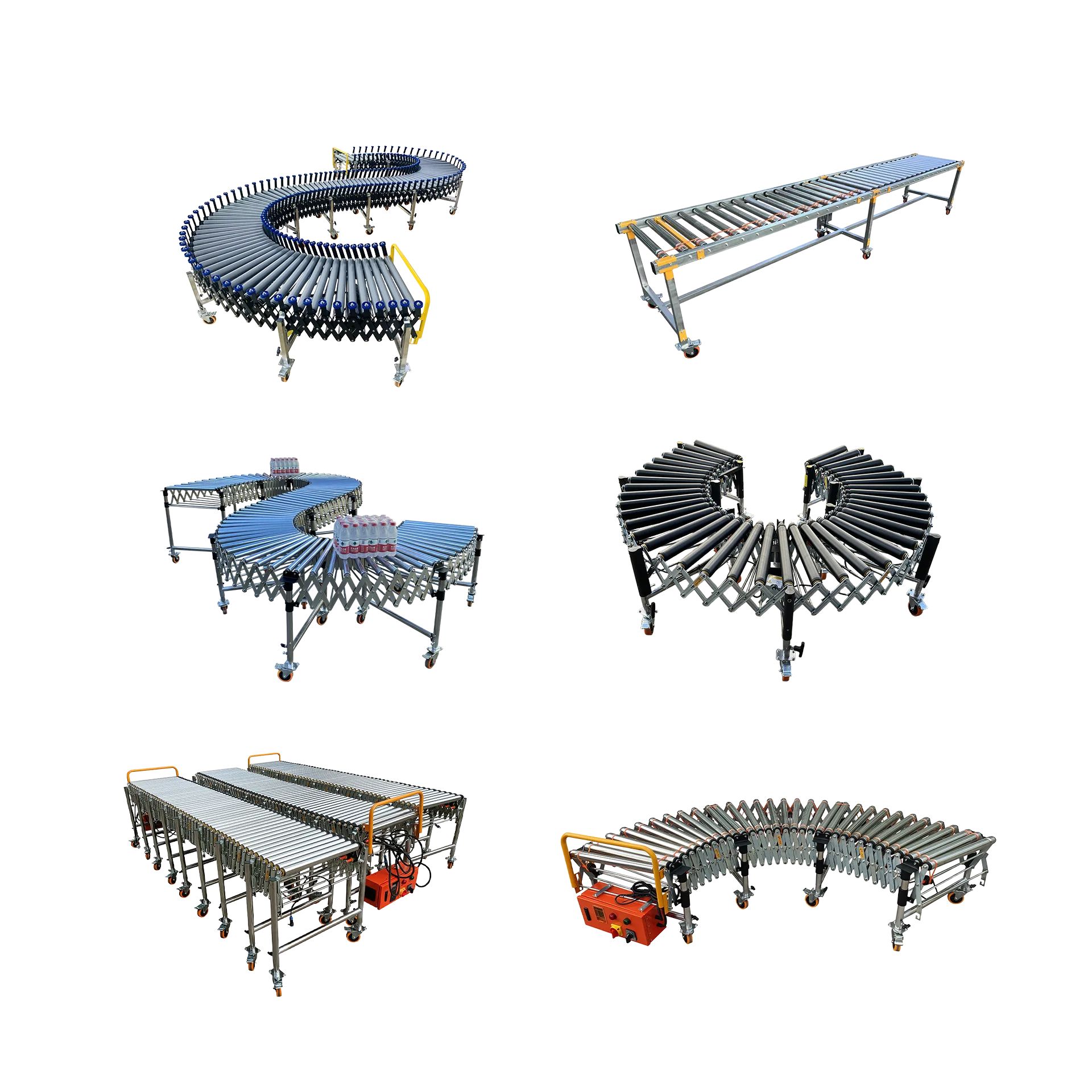


Roller conveyors consist of a series of rollers mounted in a frame that enable smooth movement of products from one point to another. These essential handling systems can be configured with different roller materials, sizes, and drive mechanisms to accommodate diverse load requirements and operational needs.
Types of Roller Conveyor Systems
Our extensive product line encompasses various roller conveyor types, each engineered for specific applications:
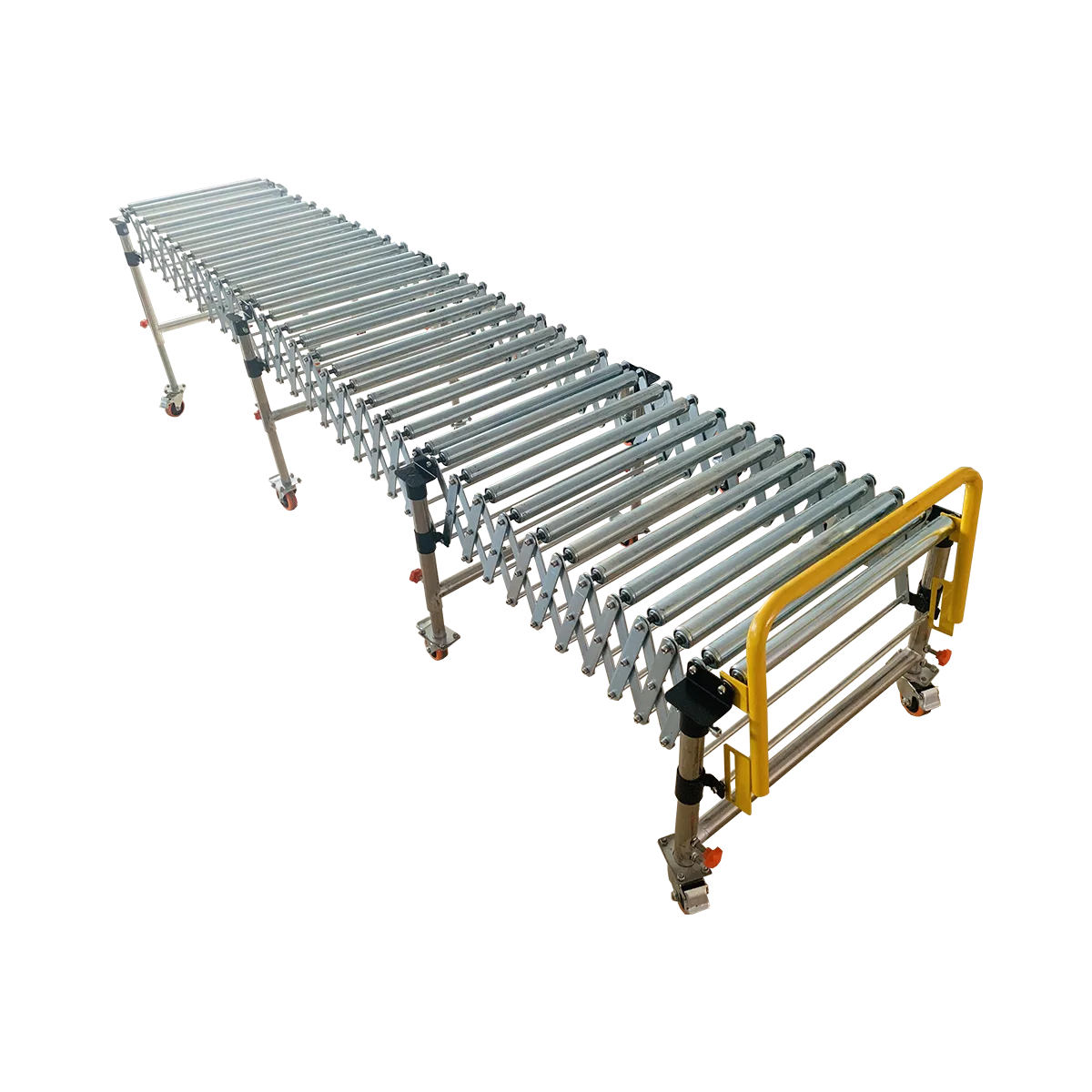
Gravity Roller Conveyor
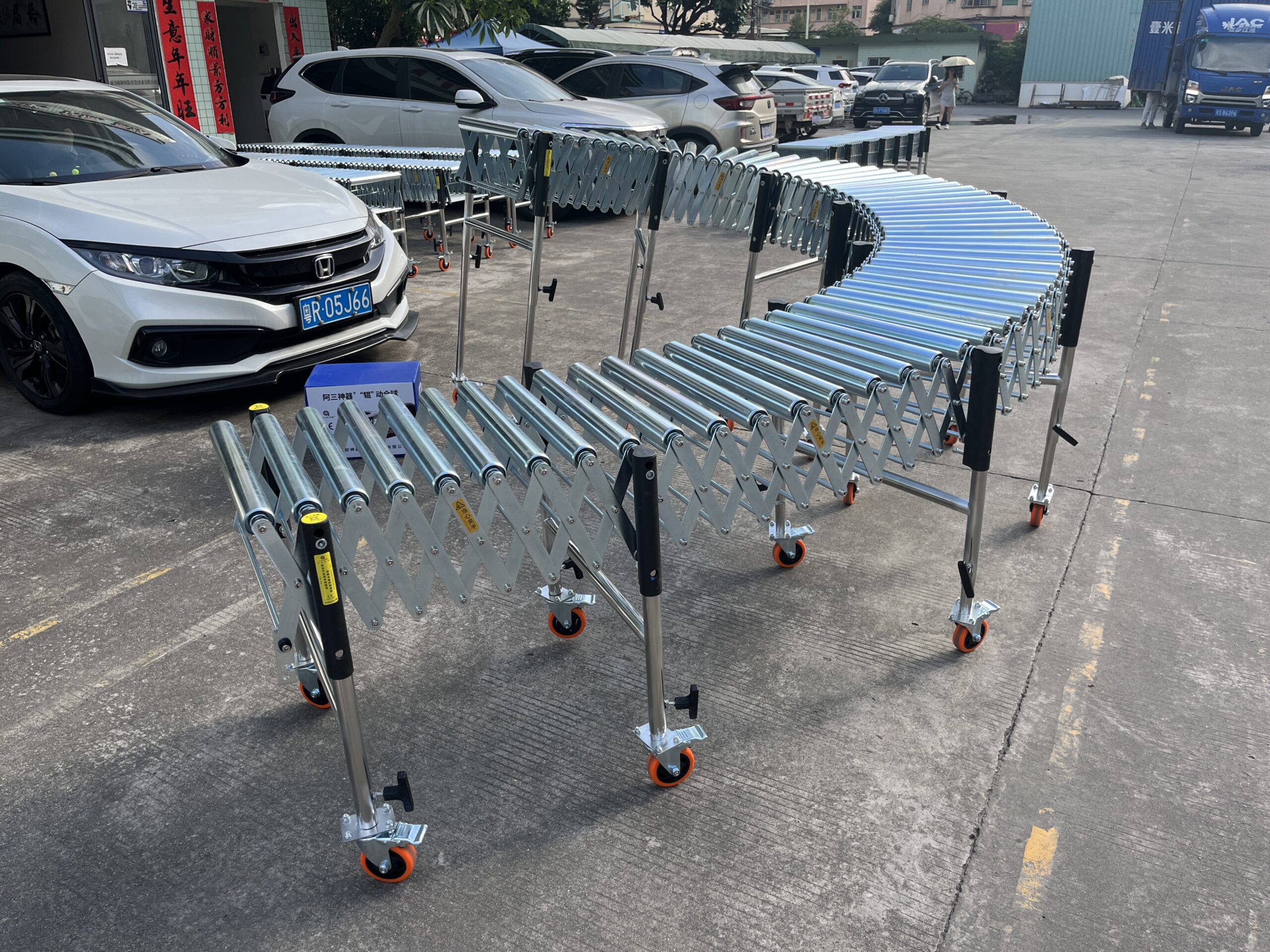


Gravity roller conveyors utilize natural gravity to move products along a slight incline. These cost-effective solutions require no power source and are ideal for simple material transport.
Key specifications:
- Roller diameter options: 38mm or 50mm
- Loading capacity: 50 kg/m
- Expandable design: 1:3 extension ratio
- Adjustable height with various leg options
- Available widths: 500/600/800 mm
These systems are perfect for environments seeking energy efficiency and minimal maintenance requirements.
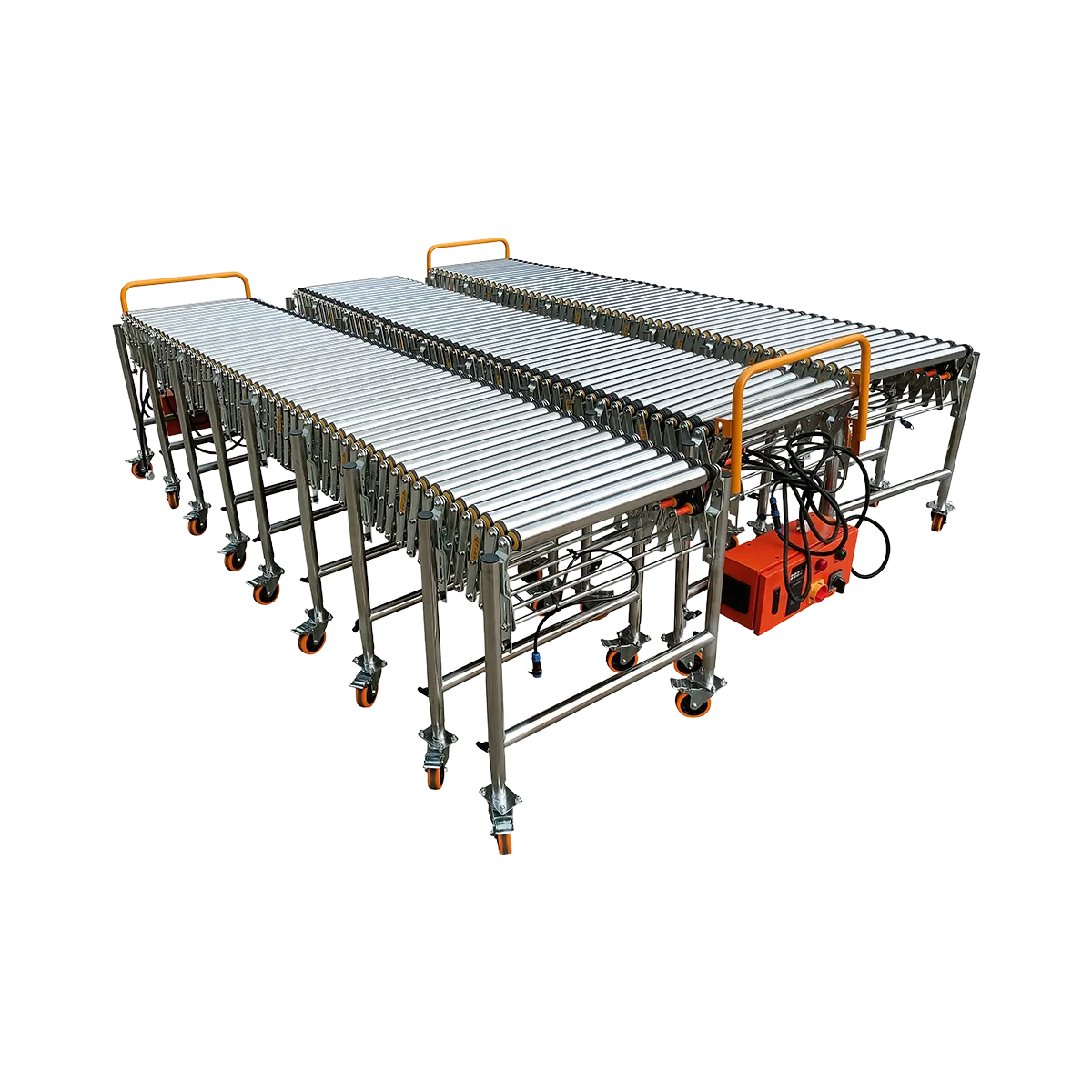
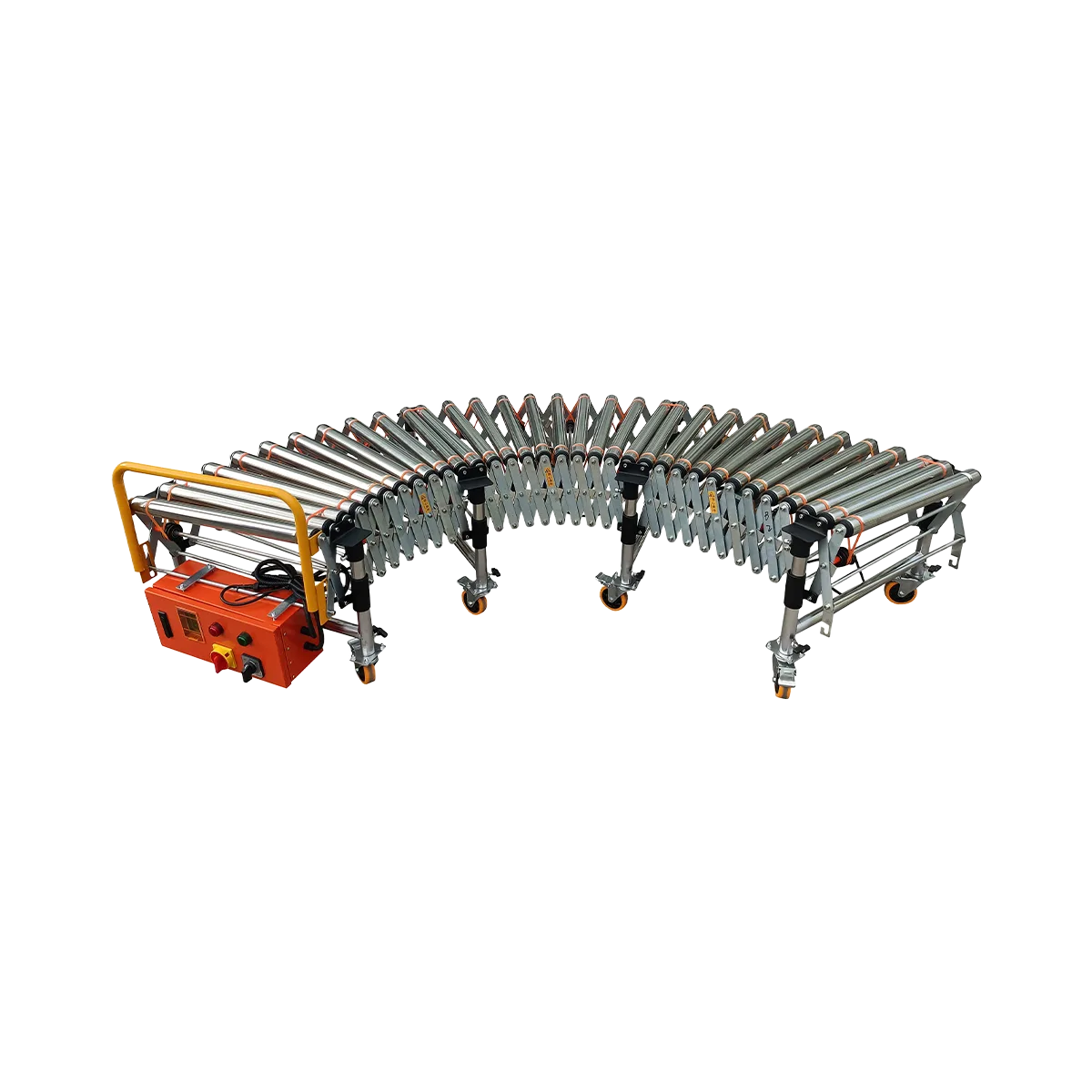
Powered Roller Conveyor
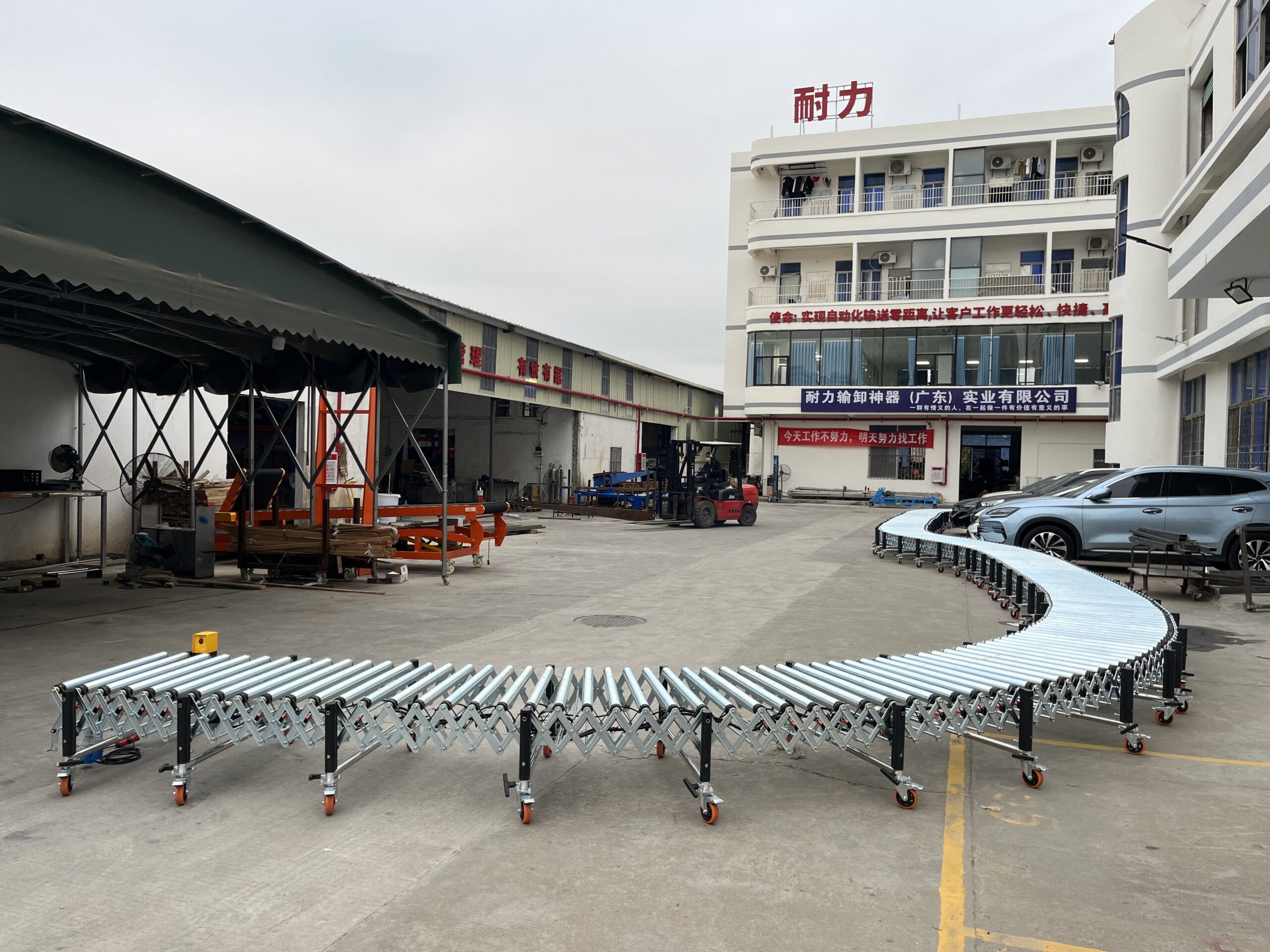


As a leading roller conveyor supplier, we provide powered roller conveyor systems that use motorized drive mechanisms for horizontal or inclined transport, offering precise control over product movement.
Our powered roller conveyors feature:
- Multiple drive options: O-belt or poly-V belt systems
- Loading capacity: 80-100 kg/m
- Speed control: 0.3-40 m/min (adjustable)
- Extension ratios from 1:3 to 2:3
- Available in various section lengths (1500mm, 2000mm, 3000mm)
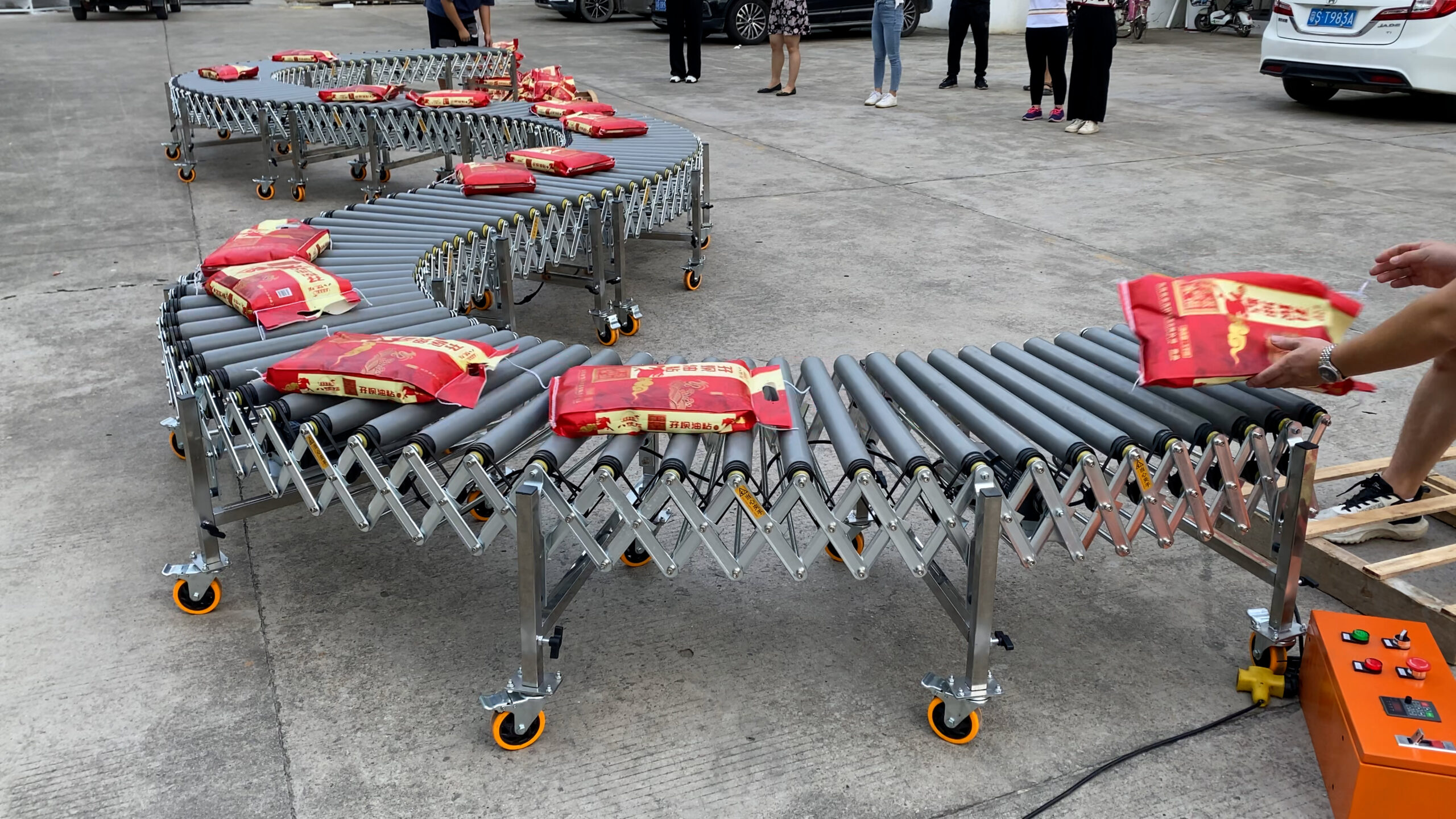


Powered Rubber Roller Conveyor


These specialized conveyors feature PVC-wrapped rollers specifically designed for transporting soft-packaged goods with enhanced grip and protection.
Notable features include:
- Loading capacity: 120 kg/m
- Speed: 40 m/min
- Poly-V belt drive system
- 1:3 extension ratio
- Particularly suited for soft packaging materials
Applications and Industries
As an experienced roller conveyor factory, we’ve developed solutions for numerous industries and applications:
Warehousing and Distribution
- Order fulfillment centers
- Cross-docking operations
- Staging areas and loading zones
- Parcel sorting facilities
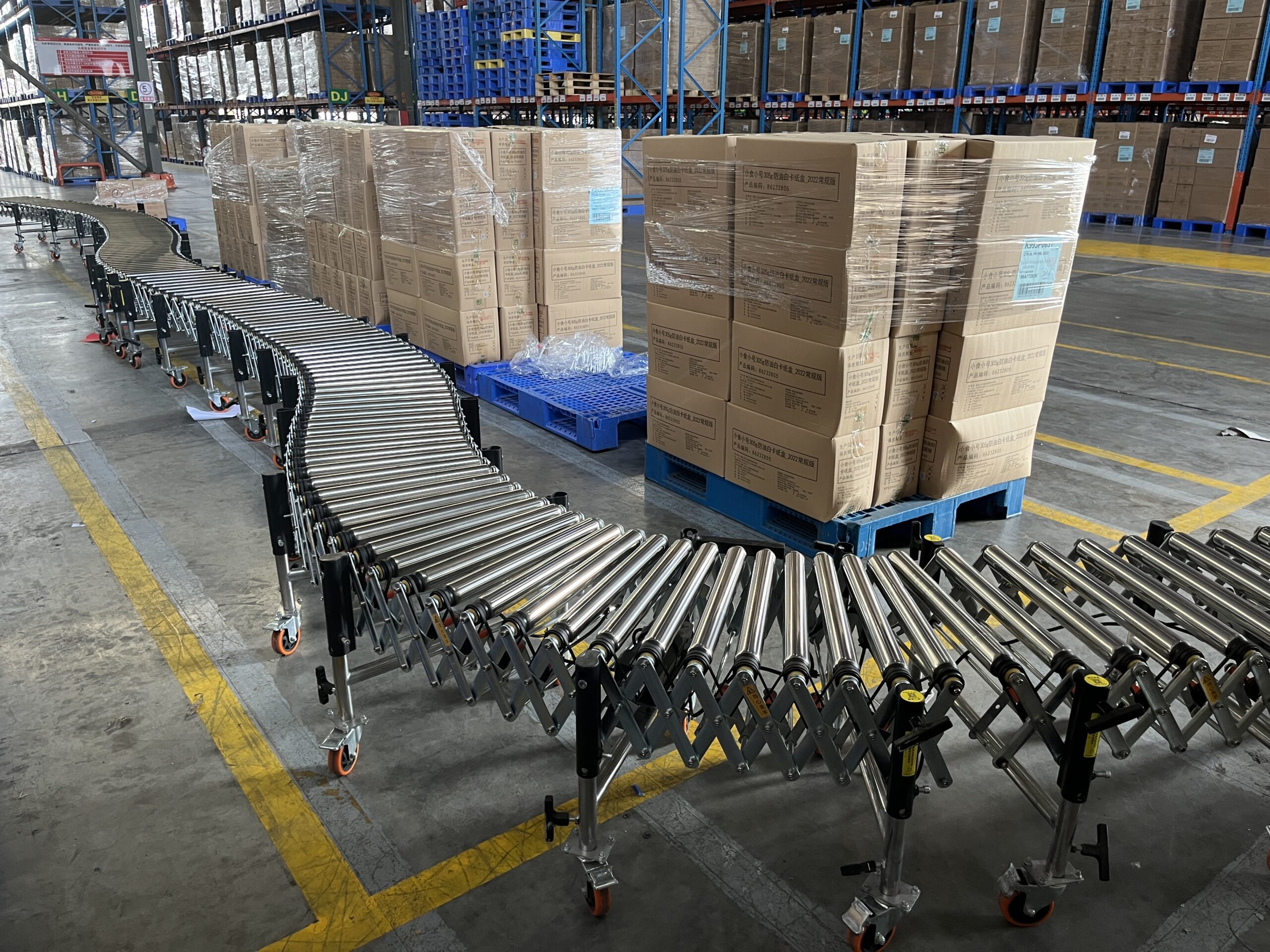


Logistics and Transportation
- Container loading/unloading
- Truck loading systems
- Last-mile distribution centers
- parcel handling system integration
Retail and E-commerce
- Distribution center operations
- Returns processing
- Packaging areas
- Order consolidation zones
Food and Beverage
- Packaged product handling
- Case movement systems
- Palletizing operations
- Distribution centers


Key Features and Advantages
Our roller conveyor systems deliver significant operational benefits:
Efficiency Improvements
- Reduced manual handling requirements
- Faster product movement
- Continuous flow operations
- Lower labor costs
Flexibility and Adaptability
- Adjustable heights for various working environments
- Expandable lengths to fit changing requirements
- Mobile options with locking casters
- Modular designs for system reconfiguration
Durability and Quality
- Industrial-grade materials throughout
- High-quality bearings for smooth operation
- Robust frame construction
- Reliable drive components in powered systems
Cost Effectiveness
- Lower maintenance requirements than complex systems
- Energy efficiency (especially gravity systems)
- Long service life (5-10+ years with proper maintenance)
- Scalable investment options


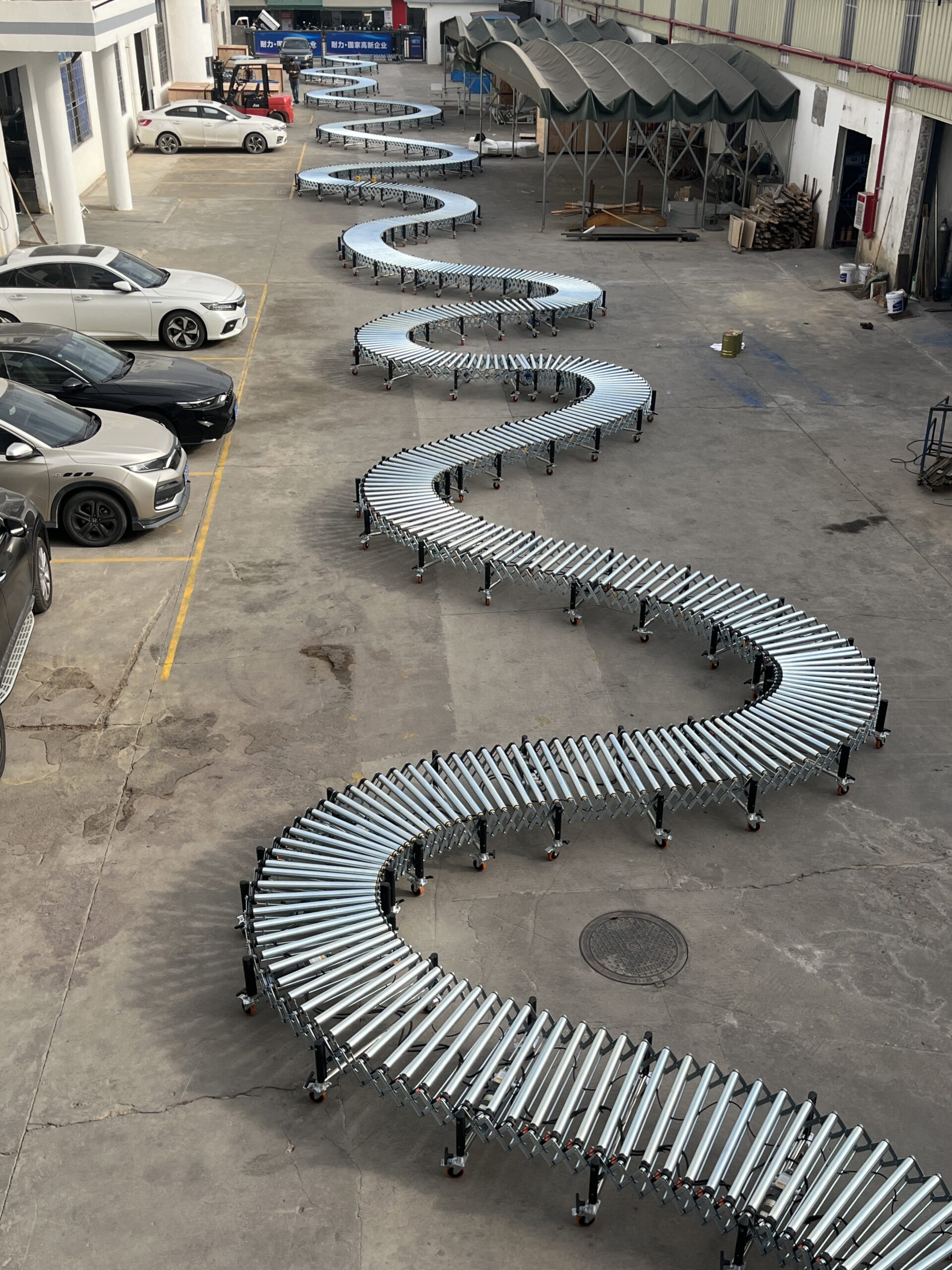
Selecting the Right Roller Conveyor
When choosing the optimal roller conveyor system, consider these critical factors:
- Product characteristics – Weight, dimensions, and bottom surface condition
- Required throughput – Volume and speed requirements
- Environmental conditions – Temperature, moisture, and cleanliness
- Available space – Both operational and storage considerations
- Integration requirements – Connection with existing systems
- Power availability – For powered versus gravity systems
- Budget constraints – Initial investment and ongoing operational costs
Our engineering team can help assess your specific requirements and recommend the most appropriate conveyor system configuration.


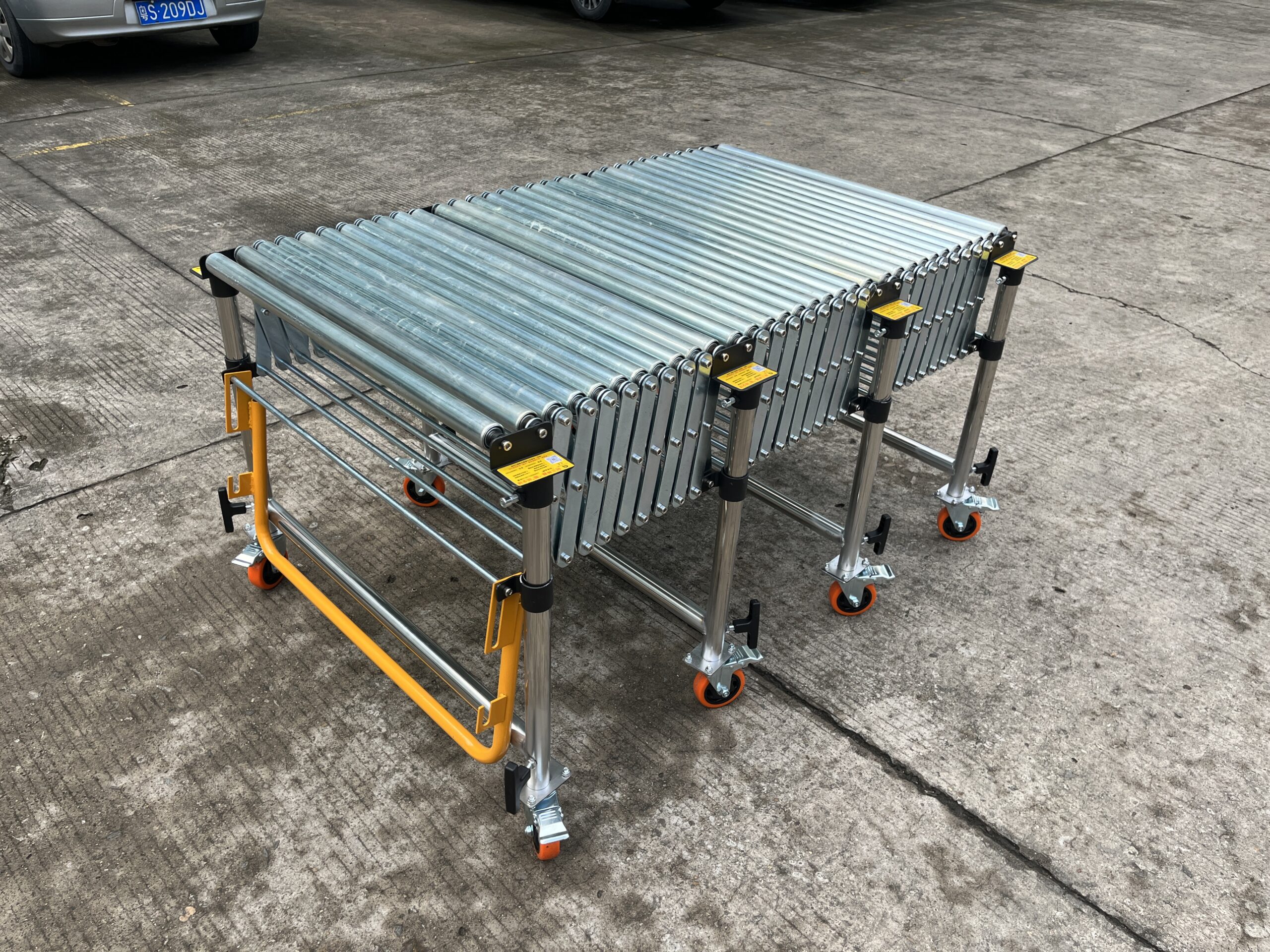
Customization Options
As a professional roller conveyor manufacturer, we offer extensive customization capabilities:
- Custom widths to match specific product dimensions
- Special roller materials for unique applications
- Integration accessories for system connections
- Specialized coatings for harsh environments
- Control system modifications for unique operational needs


Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between powered and gravity roller conveyors?
Gravity roller conveyors use inclines and natural gravity for product movement, requiring no power source but limited to downward or horizontal (with manual pushing) transport. Powered roller conveyors use motors to drive rollers, allowing precise speed control, horizontal transport, and bidirectional movement.
How do I determine the correct width for my roller conveyor?
Choose a conveyor width that is 50-100mm wider than your widest product. For mixed product sizes, base width on the largest items. Standard widths include 500mm, 600mm, and 800mm, with 600mm being the most common for standard boxes.
What maintenance is required for roller conveyor systems?
Gravity systems require checking roller movement, frame connections, and bearing condition. Powered systems additionally need drive belt tension inspection, electrical connection verification, and motor maintenance. Regular cleaning and lubrication of bearings are recommended for all systems.
Can roller conveyors handle curved or turning sections?
Yes, roller conveyors can incorporate turns through fixed-angle turning sections, flexible curves, or transfer tables. Proper design considers turning radius, incline adjustments, and guide systems to ensure smooth product flow through directional changes.
What is the typical lifespan of a roller conveyor system?
With proper maintenance, roller conveyor systems typically last 5-10+ years. Framework components generally have a 12-month warranty, while wear items like belts have shorter warranty periods (6 months). Regular maintenance significantly extends operational lifespan.
Conclusion
Our high-quality roller conveyor solutions offer exceptional value for businesses seeking efficient material handling systems. Whether you need a simple gravity system for small operations or complex powered systems for high-throughput environments, our experienced team can design and implement the perfect solution for your specific requirements.
As a trusted roller conveyor supplier and manufacturer, we’re committed to delivering products that improve your operational efficiency while providing outstanding durability and return on investment.