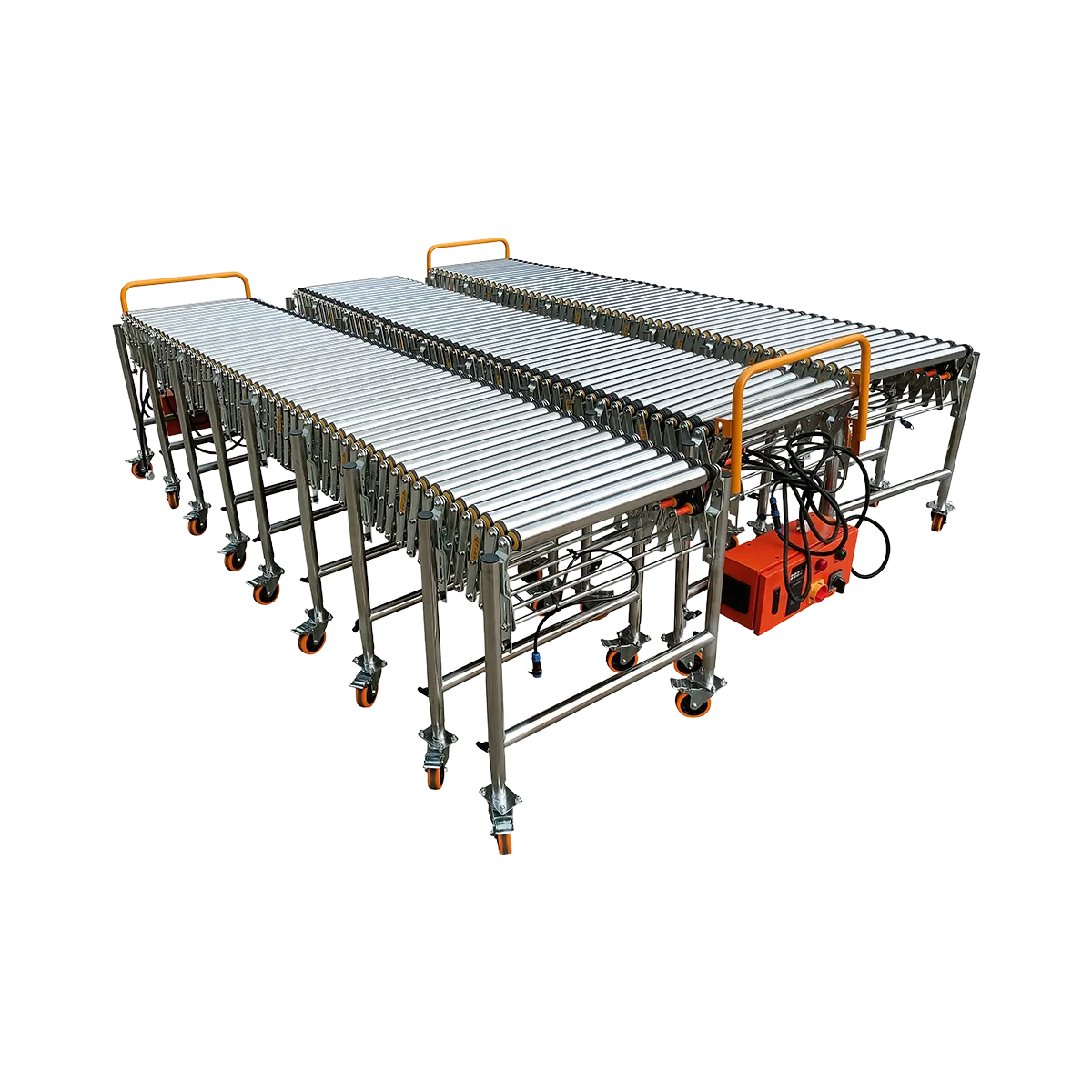
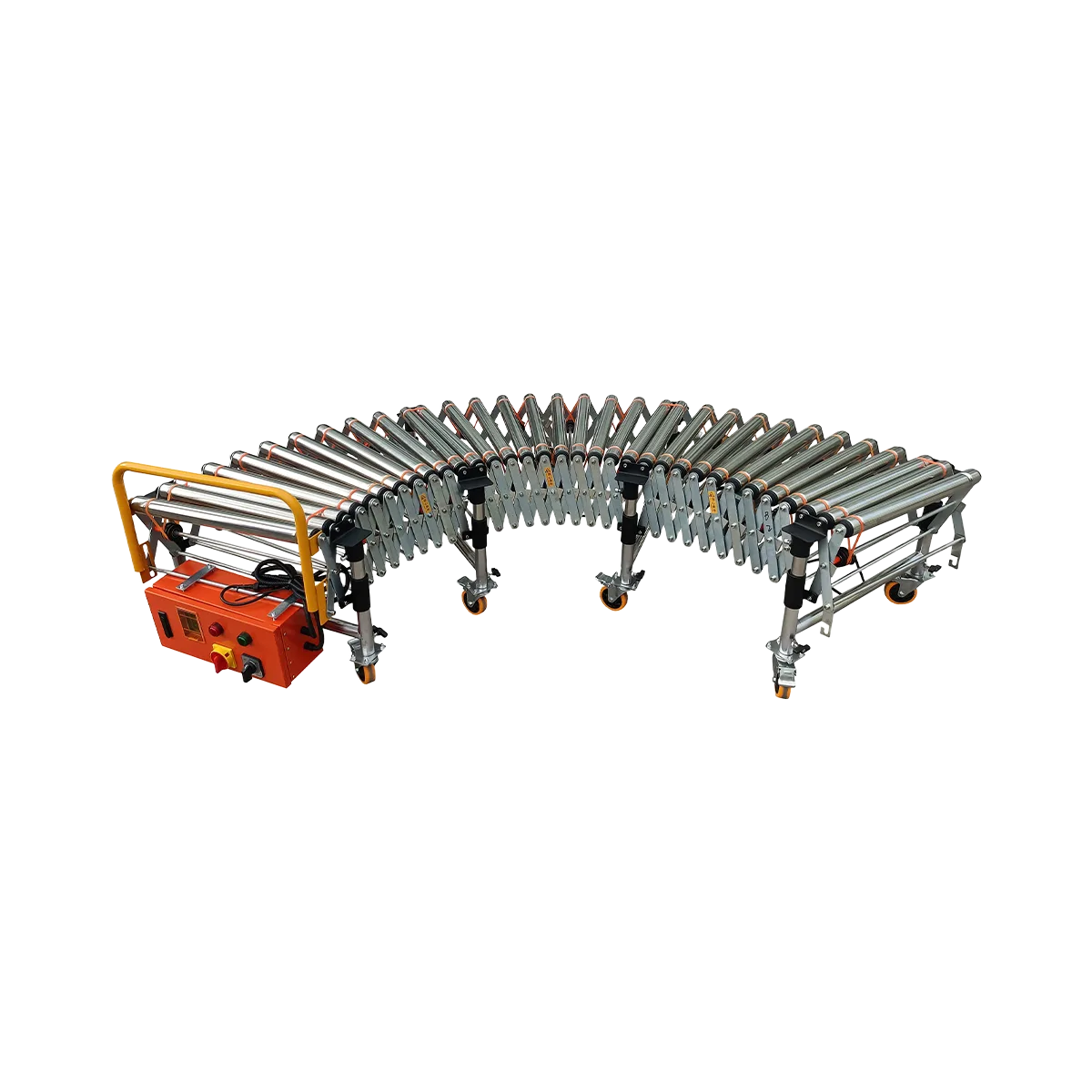
Powered Roller Conveyor Manufacturer
Home > Roller Conveyor > Powered Roller Conveyor
Our Powered Roller Conveyor Products
525 mm
1500 mm
80 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
700 mm
2000 mm
100 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
1050 mm
3000 mm
80 kg/m
Flat-bottomed Goods
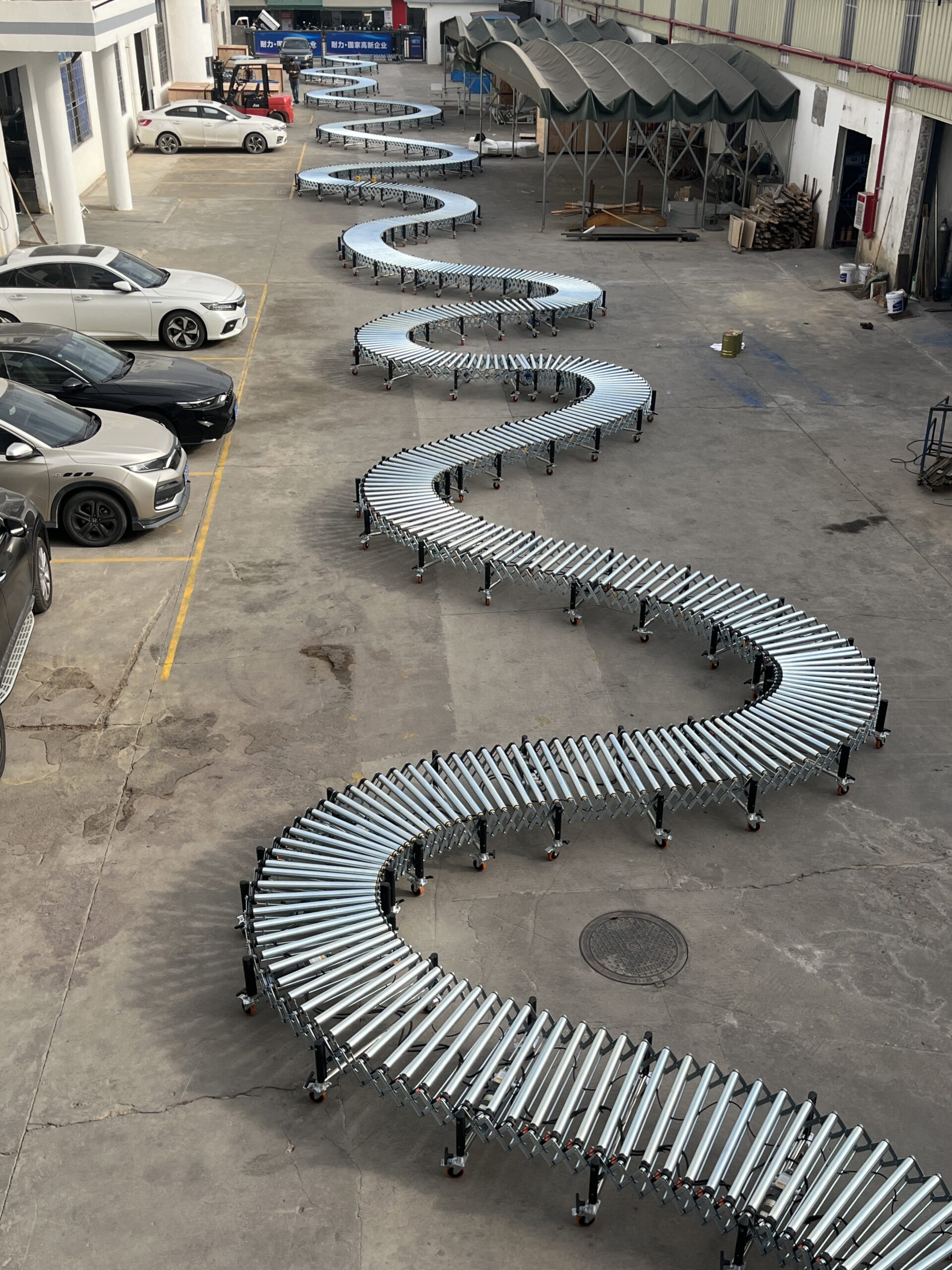
Powered roller conveyors are essential motorized material handling equipment designed to transport packages, boxes, and various goods with minimal manual intervention. Unlike gravity-driven systems, these conveyors feature integrated motors that drive the rollers, enabling efficient horizontal movement of products regardless of weight distribution or surface friction. As a leading powered roller conveyor manufacturer, we provide versatile solutions that significantly enhance productivity in warehouses, distribution centers, and production facilities worldwide.
Our motorized roller conveyor systems feature adjustable heights, extendable lengths, and robust construction, making them ideal for both permanent installations and temporary operations requiring frequent reconfiguration. With load capacities ranging from 80-100 kg/m and adjustable speeds up to 40 m/min, our systems deliver reliable performance across diverse industrial applications.
Types of Powered Roller Conveyors
O-Type Belt Driven Conveyors
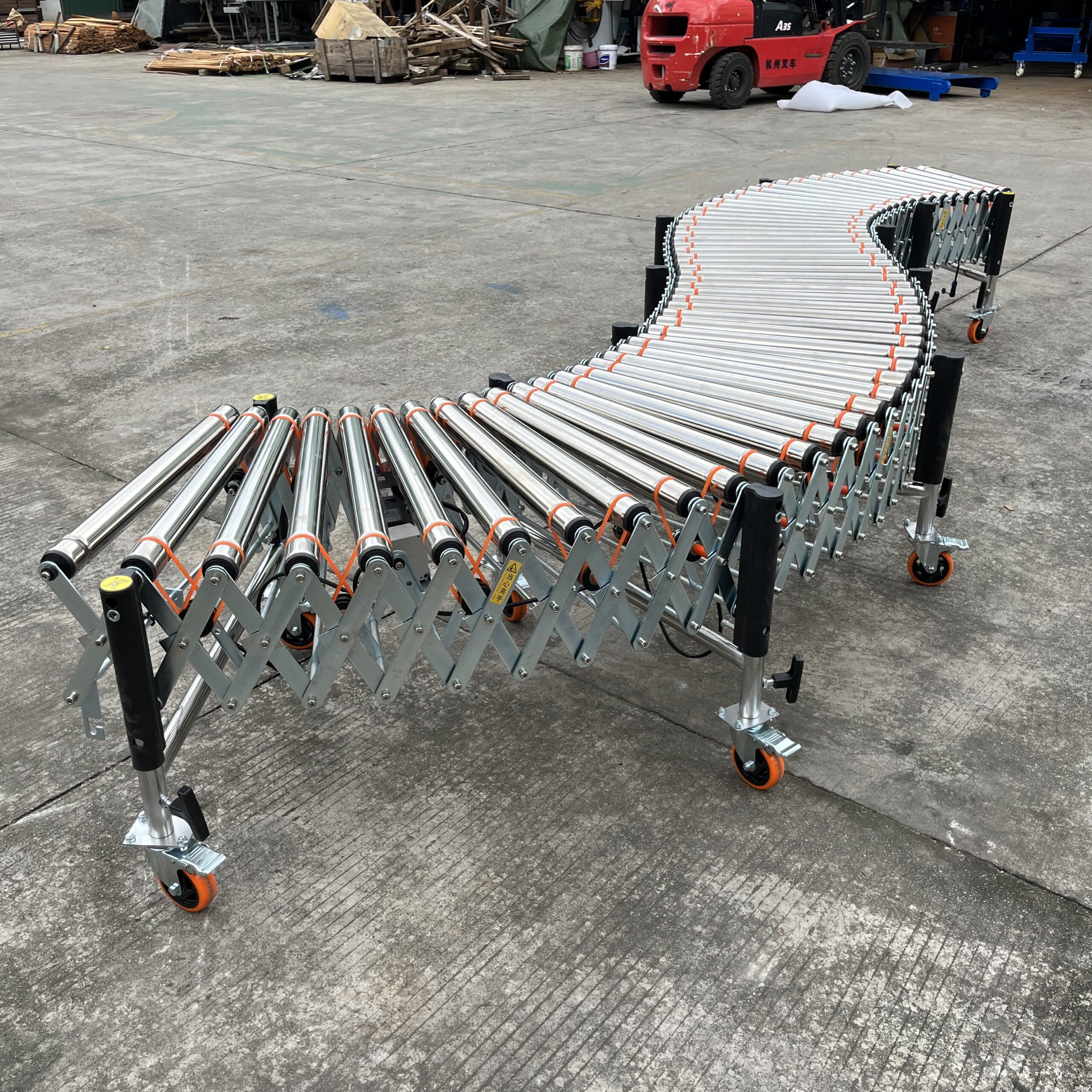

The O-type belt driven powered roller conveyor offers an economical solution for light to medium-duty applications. Each section extends from 525mm to 1500mm (1:3 ratio), making it highly adaptable to changing space requirements. These systems feature:
- Load capacity of 80 kg/m
- Simple maintenance requirements
- Quieter operation compared to other drive systems
- 50mm diameter rollers with ≥1.5mm thickness
- Ideal for standard packaging and regular-shaped items
Multi-Wedge Belt Driven Conveyors
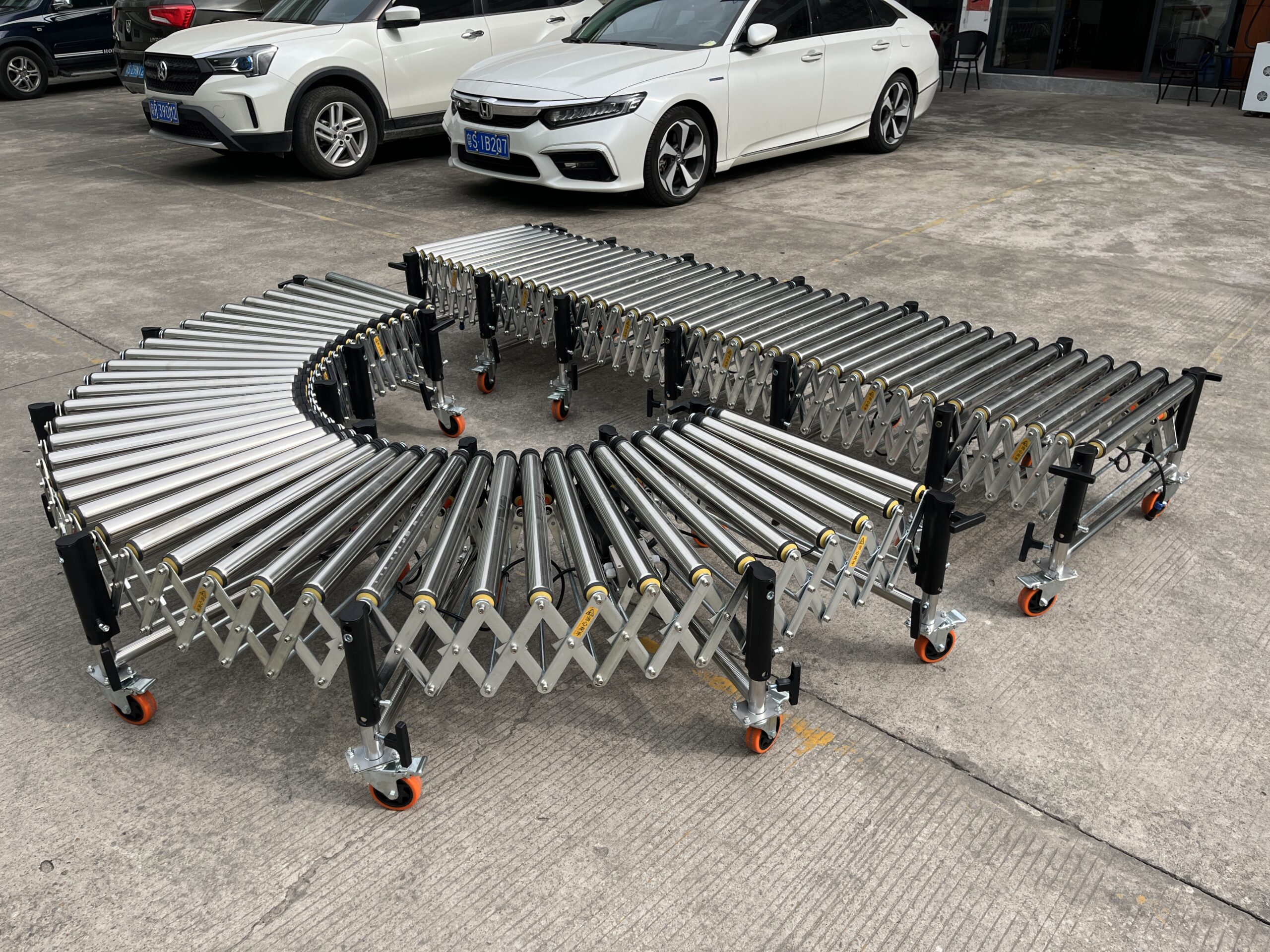

For more demanding applications, our multi-wedge belt driven conveyors provide enhanced power transmission efficiency and superior load capacity. Available in two configurations:
- 2000mm/section model: Extends from 700mm to 2000mm with exceptional 100 kg/m load capacity
- 3000mm/section model: Our longest single-section option extends from 1050mm to 3000mm with 80 kg/m capacity
Multi-wedge systems deliver:
- Higher transmission efficiency
- Reduced belt slippage
- Extended service life
- Better stability at higher speeds
- Superior performance for medium to heavy loads

Key Features and Benefits
As a professional powered roller conveyor supplier, we focus on delivering maximum value through thoughtfully designed features:
Adaptability and Flexibility
- Extendable length (1:3 ratio for most models)
- Adjustable height options: 450-680mm, 550-820mm, 750-1200mm, or 900-1500mm
- Available widths: 500mm, 600mm, and 800mm to accommodate various package sizes
Performance and Reliability
- Speed range of 0.3-40 m/min through variable frequency control
- Bidirectional operation capability
- Emergency stop functionality
- High-quality 201 stainless steel components
- 12-month frame warranty and 6-month belt warranty
Operational Efficiency
- Reduces manual handling requirements
- Streamlines workflow between workstations
- Integrates easily with existing systems
- Quick setup and reconfiguration
Mobility and Convenience
- 4-inch casters (width 30mm, height 120mm) with full braking capability
- Simple control panel with forward/reverse, emergency stop, and speed control
- Modular design allows connection of multiple conveyor sections
Applications and Industries
Our motorized roller conveyor systems excel in diverse operational environments:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Warehousing & Distribution | Package routing, order fulfillment, truck loading/unloading |
| E-commerce | Sortation processes, packing stations, dispatch areas |
| Manufacturing | Production line transfers, assembly operations, end-of-line packaging |
| Food Processing | Packaged product transport, inspection stations, packaging areas |
| Retail Logistics | Store replenishment operations, returns processing |
| Parcel Services | Distribution centers, transfer stations, sortation systems |
Technical Specifications
| Specification | O-Type Drive (1500mm) | Multi-Wedge (2000mm) | Multi-Wedge (3000mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collapsed Length | 525mm | 700mm | 1050mm |
| Extended Length | 1500mm | 2000mm | 3000mm |
| Extension Ratio | 1:3 | 2:3 | 1:3 |
| Speed Range | 0.3-40 m/min | 0.3-40 m/min | 0.3-40 m/min |
| Load Capacity | 80 kg/m | 100 kg/m | 80 kg/m |
| Roller Diameter | 50mm | 50mm | 50mm |
| Motor | 120W reducer | 120W reducer | 120W reducer |
| VFD Options | 0.75/1.5/2.2 kW | 0.75/1.5/2.2 kW | 0.75/1.5/2.2 kW |
| Voltage | 380V/220V | 380V/220V | 380V/220V |
Why Choose Our Powered Roller Conveyors?
As a trusted powered roller conveyor factory, we offer distinct advantages:
- Quality Construction: Our conveyors feature high-grade stainless steel frames with ≥1.3mm thickness and Q345 steel components with ≥3.5mm thickness
- Customization Options: Multiple width, length, and height configurations to match specific requirements
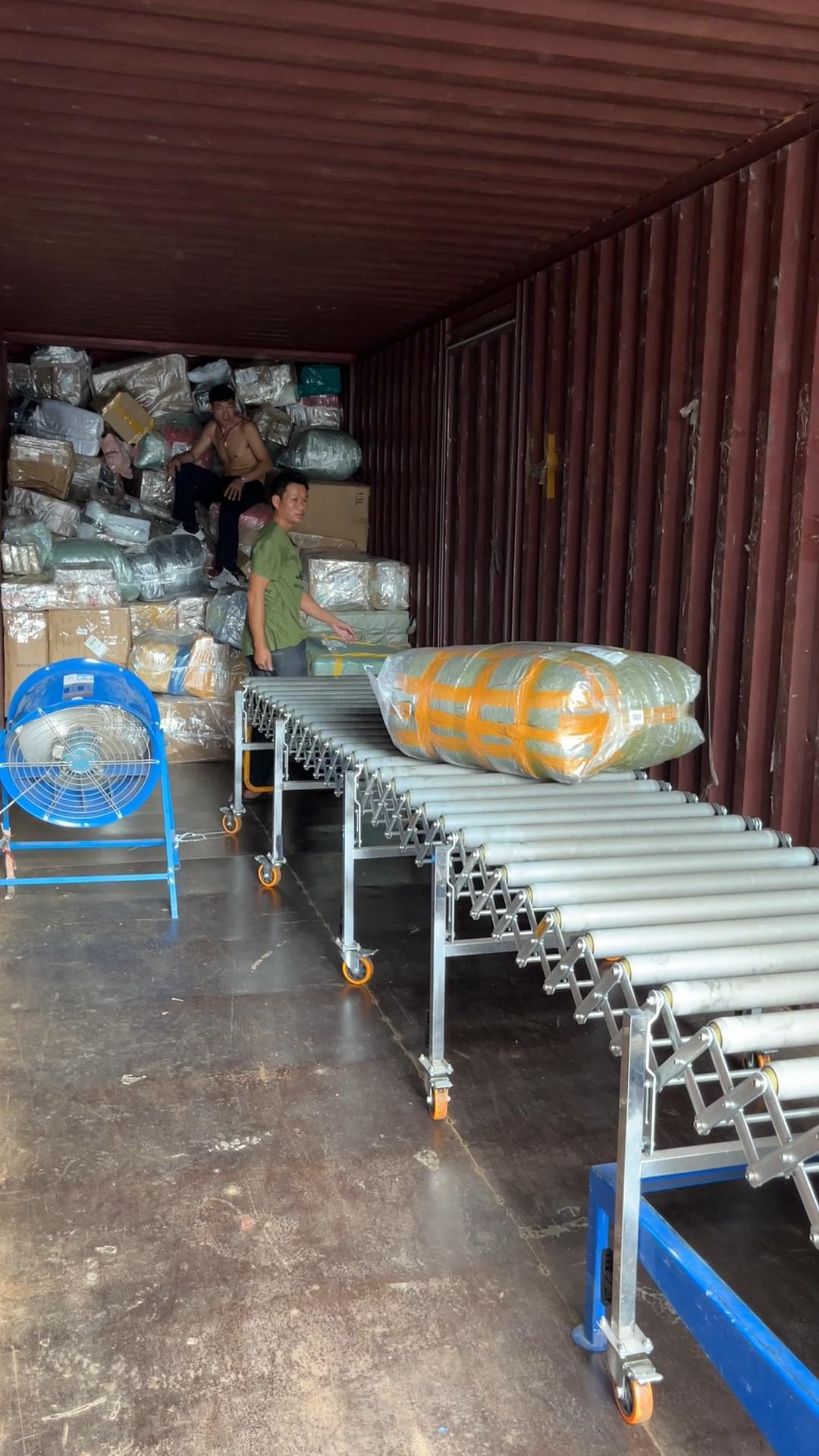
- System Integration: Seamless connectivity with other conveyor types including gravity roller conveyors, telescopic conveyors, and hydraulic conveyors
- Operational Efficiency: Reduced labor requirements, typically needing just two operators for loading and unloading
- Maintenance Simplicity: Easy-to-replace drive belts, accessible roller bearings, and straightforward electrical components

Selecting the Right Powered Roller Conveyor
When choosing the optimal motorized roller conveyor for your operation, consider these key factors:
Weight Requirements
- For loads up to 80 kg/m: Select either O-type drive or 3000mm multi-wedge systems
- For heavier loads up to 100 kg/m: Choose the 2000mm multi-wedge system
Space Constraints
- Limited space: 1500mm O-type drive offers the most compact collapsed size
- Maximum extension needed: 3000mm multi-wedge provides greatest single-section coverage
- Frequent repositioning: Consider total weight (O-type systems are lighter)
Material Types
- Standard packaging: Any model works effectively
- Special shapes: Consider roller spacing and diameter
- Budget considerations: O-type drive systems typically offer lower initial investment

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between O-type and multi-wedge drive systems?
O-type drive systems have simpler maintenance, lower noise, and lower costs but less load capacity. Multi-wedge systems offer higher efficiency, greater load capacity, less slippage, longer service life, and better stability at high speeds.
How long do powered roller conveyor drive belts typically last?
O-type drive belts typically require replacement every 6-12 months depending on usage frequency. Multi-wedge belts generally last 12-18 months before needing replacement.
Can powered roller conveyors connect with other conveyor types?
Yes, our powered roller conveyors integrate seamlessly with gravity skate wheel conveyors, hydraulic lift conveyors, and other material handling equipment through transition plates or direct connections.
What maintenance does a powered roller conveyor require?
Regular maintenance includes weekly visual inspections, monthly drive belt checks, quarterly bearing lubrication, and quarterly electrical system checks. Replacement parts primarily include drive belts and roller bearings.
How do I select the appropriate width for my powered roller conveyor?
Choose a conveyor width at least 100mm wider than your widest package. For standard applications, 600mm is most common, while 800mm accommodates larger items, and 500mm is suitable for smaller packages and space-constrained environments.
Conclusion
As an experienced powered roller conveyor manufacturer, we understand the critical role these systems play in modern material handling operations. Our motorized conveyor solutions combine durability, flexibility, and performance to deliver exceptional value across various industries and applications. Whether you need a single conveyor section or a comprehensive integrated system, our robust product line offers the right solution to enhance your operational efficiency.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our premium motorized roller conveyor systems can transform your material handling processes.